How to do pollution control in the fermentation process
Analyze the reasons for the bacteria in the fermenter , sum up the experience and lessons of preventing the fermentation of the bacteria, eliminate the fermentation of the bacteria before the occurrence, prevent the accident, and actively subdue the bacteria in the fermentation industry.
Causes of contamination of bacteria in the fermentation industry
1. Classification of bacterial strains and conditions for survival of bacteria
Many of the bacteria have similar growth conditions to our industrial strains, so they can grow well in industrial fermentation. We must control the contamination of the bacteria, and we must know the growth conditions and metabolic pathways of the bacteria. The most susceptible bacteria in the fermentation process are fungal yeasts, molds, etc., Bacillus brevis, cocci, etc. in bacteria and virus phage. Zui suitable growth temperature means that at this temperature, the metabolism of microorganisms reaches a large rate of zui, and the growth temperature of general microorganisms is 25 to 35 °C. Understanding the suitable growth temperature of each species of Zui has certain reference value for analyzing the causes of bacterial infection. Microorganisms die when they grow above their high growth temperature. The mechanism by which microorganisms die at high temperatures is caused by the loss of activity of the enzymes after heat. We use lethal temperature and lethal time as the standard. Mastering the lethal temperature and lethal time of various microorganisms facilitates the sterilization operation. Under normal circumstances, Escherichia coli, pneumococci and yeast can die at about 10 °C for 10 min, while Bacillus subtilis kills at 100 °C for 17 min, and Bacillus thermophilus requires 12 min at 120 °C to kill. The pH in the microbial growth environment is closely related to the activity of microorganisms. The change of pH may cause the accumulation of certain metabolites, and if the pH is mutated, it may be due to the infection of certain bacteria. In general, the pH range of bacterial growth is 4-9, and Zui is 7 or slightly alkaline. The pH range for growth of mold and yeast is 2-7, and Zui is suitable for 5 or slightly acidic. Understanding the pH range of various microbial growth is useful for identifying the cause of the infection and controlling the fermentation conditions.
2, the cause of the bacteria
Since many aspects of industrial fermentation are semi-open, in many cases, bacterial infection is an inevitable problem, but there are many reasons for bacterial infection, mainly human factors caused by poor management, seed carriers, unreasonable equipment structure, and process pipelines. Unreasonable installation, leaking or dead spots in the equipment, and airborne bacteria.
(1) Seed carrier. According to the long-term experience, in the early stage of fermentation, especially within 0 ~ 6h, there is little infection, and after 10h or 20h, the number of bacteria will gradually increase or even increase suddenly. Seed-contaminated spores may be caused by incomplete sterilization. If the yeast or mold is contaminated, it may be caused by seed. In order to clarify whether the bacteria are caused by the seed, the small amount of the seed liquid remaining in the inoculum is continuously cultured after the inoculation to observe whether it is a seed carrier. In the case of a small number of contaminating bacteria, and the contaminated bacteria are sensitive to the antibiotics secreted by the bacteria produced during the cultivation process, it is difficult to culture in this case by sterility test; but in the seed tank or fermenter, Continue to grow, multiply, and even harm the fermentation, this situation should be bacteria-borne.
(2) Equipment factors. The loopholes in the equipment during fermentation production are also an important factor in the dyeing. In the structure of the equipment, the factors that constitute the fermentation bacteria are as follows: the equipment structure is unreasonable, the equipment installation is unreasonable, the equipment itself leaks, dead angles and A vulnerability in device management. In addition, the fermentation method is unreasonable and easy to stain. Equipment leaks may be caused by chemical corrosion, electrochemical corrosion, abrasion, and improper handling of the equipment. Unferable fermentation equipment can also be contaminated, such as steam systems, sterile air systems, material disinfection systems, cold water systems, etc. The temperature of the steam, the pressure, and the amount of condensed water in the steam will affect the quality of the steam. Due to the large condensed water content in the wet saturated steam, the steam temperature is low, and the pressure fluctuation is large, which may cause the sterilization temperature to fall short of the bacteria. Time and lethal temperature cause fermentation to contaminate the bacteria. Excessive steam lines, excessive bypasses, recycling, or unsterilized equipment can cause bacterial contamination. The main factors causing the bacteria in the air system are the oil in the air, the improper installation of the total air system, and the lack of regular inspections. The bacteria caused by the material disinfection system are mainly dead cells of the equipment, or are not regularly checked.
(3) Human factors. The human factor causing the infection refers to the operator's operation method, the quality of the operation, and the responsibility of the operator's work, etc., which can be avoided and not avoided. Human factors include not checking the density before entering the tank, infringing the operation rules, lacking the inspection quality of the inspection quality, unskilled operation or mistakes. The contamination of bacteria caused by human factors must be paid enough attention, because many times the artificially caused bacteria are often caused by some knowing, numbness or luck of the operators, and once infected, huge economic losses will be given to people. Take a deep painful lesson.
Technology for controlling bacteria in the fermentation industry
After understanding most of the causes of infection, we should improve all aspects of the cause of the infection, and reduce the risk of infection to low. The * step to prevent contamination of the bacteria is to do the disinfection and sterilization work before entering the tank.
1. Sterilization technology in the fermentation industry
(1) Sterilization of the medium. 3. The common sterilization methods for the medium include dry heat sterilization, moist heat sterilization, radiation sterilization, chemical sterilization, filtration sterilization, flame sterilization, ozone sterilization, etc.
At present, the use of zui in the fermentation industry is mostly wet heat sterilization. Wet heat sterilization utilizes high-temperature saturated steam to have a strong penetrating ability, and at the same time, it will release a large amount of heat of condensation when condensing, and raise the temperature of the material to coagulate and denature the protein in the microorganism, thereby killing various microorganisms. Method of sterilization. Sterilization conditions are usually 121 ° C for 30 min. The moist heat sterilization has the characteristics of easy steam source, large latent heat and strong penetrating ability, and has the advantages of good sterilization effect and low operation cost compared with other sterilization methods. The dry heat sterilization method uses a dry high-temperature hot air to oxidize proteins in a microorganism to be sterilized. Commonly used dry heat sterilization conditions are incubated at 160 ° C for 1 ~ 2h. The advantage of dry heat sterilization is that it can be kept dry, but the sterilization effect is not as good as moist heat sterilization.
(2) Filtering and sterilizing air. Aerobic bacteria need to be constantly ventilated during the fermentation process to provide the oxygen needed for microbial respiration and metabolism. Most of the microorganisms in the air are bacteria and various spores. Yeasts and virions are also present. Most of them are attached to the dust of the air. The air is mainly used to remove particles from the air. The methods of air sterilization mainly include radiation sterilization, chemical sterilization, electrostatic dust removal and heat sterilization. However, for the sterilization of large flow air, fiber medium filtration sterilization method is still widely used. At present, as an air sterilization medium, there are cotton fibers, microfiber papers, and nylon fibers. When the air medium is filtered, the gap between the media is much larger than the diameter of the particles. The fiber medium retains the particle mechanism in several ways: blocking interception, inertial collision interception, and Brownian diffusion motion.
(3) Equipment and piping sterilization equipment and piping must also be sterile before use.
<1> The sterilization of empty tanks such as seed tanks, fermenters, metering tanks and feed tanks shall be carried out from the relevant passages at the bottom of each tank, so that the pressure inside the tank reaches 0.147 MPa (gauge pressure) for 45 minutes. The sterilization process should discharge air from the Russian related valves at the top of each tank and allow the steam to pass through to achieve dead angle sterilization. After the sterilization is completed, after the steam valve is closed, when the pressure in the tank is lower than the pressure of the air filter, the sterilizing air is pressurized to 0.098 MPa (gauge pressure).
<2> Sterilization of the air total filter and the sub-filter is carried out from the upper part of the air filter, and is exhausted from the upper and lower exhaust ports, and the pressure is maintained at 0.147 MPa (gauge pressure), and sterilized for 2 hours. After the sterilization is completed, the air filter is blown dry by introducing compressed air, and then kept under pressure.
<3> The sterilization tank line, defoamer line and inoculation line are generally required to have a pressure of 0.3-0.45 MPa and a holding time of 1 h.
2. Control technology of miscellaneous bacteria and measures to prevent bacterial infection
(1) Control of bacteria. For different reasons for contamination, we should take different measures to control. If the phenomenon of bacterial infection occurs, first find the cause of the infection, and then take remedial measures. Even if the batch of products cannot be recovered, the cause should be found in detail and corrected to accumulate lessons for future production.
In the case of seed-borne bacteria, in order to prevent seed-borne bacteria, it is important that the sand tube, the freezing tube, the bevel and the shake flask are strictly controlled in the preparation of the seed. In particular, the mother bottle when inoculated with liquid mycelium is a link that is easy to attract bacteria. Therefore, keeping the shake bottle clean can reduce the chance of contamination by bacteria. In the case of equipment leakage, since small leaks are difficult to find with the naked eye, it is necessary to regularly check the equipment to avoid large-scale contamination. For the materials of the equipment, corrosion-resistant materials, corrosion inhibitors, control and corrosion environment should be selected to reduce or prevent chemical corrosion. Cathodic protection can prevent electrochemical corrosion equipment.
In industrial fermentation, the problem of bacterial infection is also serious due to poor management. Good fermentation equipment and strict sterilization are prerequisites for preventing contamination. However, simply paying attention to technical operations and neglecting technical management will not achieve satisfactory antibacterial effects. The technical management of preventing fermentation and contamination is an important part of enterprise technology management. It has certain requirements for the staff, plant, sanitation, dispatching, equipment, raw materials and production operations of a fermentation plant. The special city report on fermenting bacteria should be carefully filled out in order to discuss, analyze and find out the reasons and learn lessons. Prevent it from happening again.
Phage damage is common in the fermentation industry, especially in the production of glutamic acid, enzyme preparations, antibiotics, organic solvent nuclear cheese, yogurt. The current measures for phage contamination have not reduced the hazard to zero, but it has indeed reduced the rate of infection. These measures include: regular inspection of phage, understanding of changes in its quantity and distribution; improvement of the environment, maintenance of production areas; drug control and rescue techniques; selection of anti-phage strains and their rational use.
(2) Prevention of bacterial infection measures. In different industrial production, the measures to prevent miscellaneous bacteria are not the same. It is necessary to do specific analysis in specific environments and use practical methods to reduce the infection of bacteria. Under the responsibility of the Shanghai Institute of Scientific Research, the Shanghai Brewing 4 Factory collaborated on the control of the contamination of soy bacteria in soy sauce brewing. The study found that adding proper amount of glacial acetic acid to the production of koji and koji has obvious inhibitory effects on common micrococci, streptococci, diplococcus and Bacillus subtilis, and effectively prevents the occurrence of acid koji and koji. The quality of the koji improves the hygiene of the product and improves the clarity of the soy sauce. This kind of idea of ​​preventing bacterial infection is worth learning.
(3) Development. The fermentation control technology of the bacteria is a science generated from practice, and it is a discipline that summarizes and improves the theory and then returns to practice to solve the problem. In order to eliminate the problem of bacterial infection, we must start from the basic design of the initial stage of industrial production, we must strive to achieve "zero fermentation rate design of fermentation equipment, industrial pipelines", control the risk of infection to low Zui, to prevent , prevent problems before they happen
The closed suction tube has designed for proven effective in preventing infections, reducing cross-contamination, reducing intensive care unit days and patient costs.
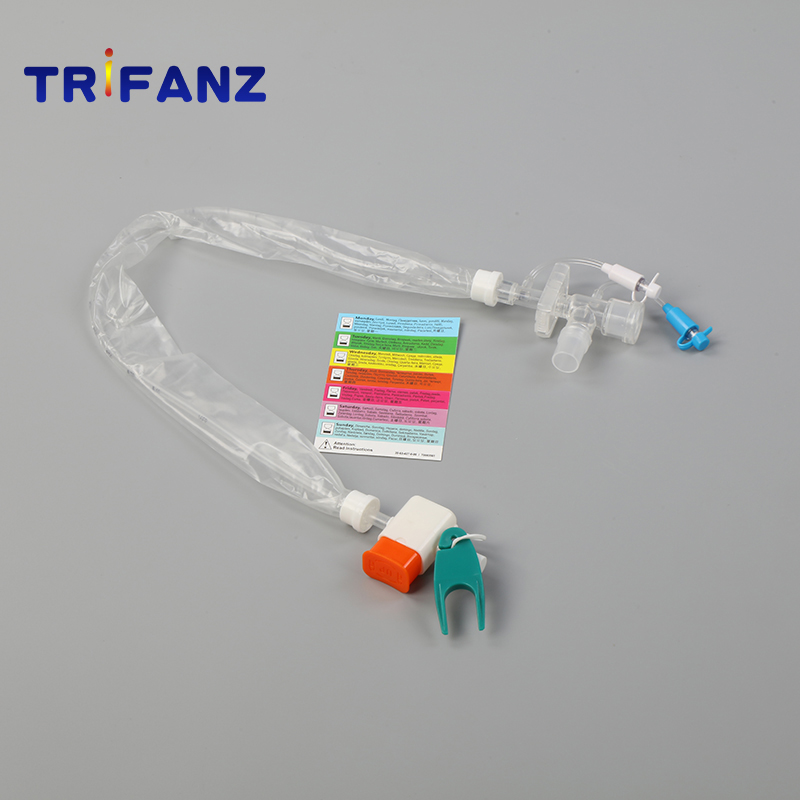
Type: Adult 72 hours closed suction tube, adult 24 hours closed suction tube, children closed suction tube
Features&Benefit
1. Allow for suctioning a patient on a ventilator without loss of PEEP or mean airway pressure.
2. Reduce oxygen desaturation by allowing constant patient ventilation.
3. Reduce the potential of infection to the clinician
4. Maintains a sealed airway to reduce exposure to secretions.
5. Eliminates patient"Spray Black"
6. Provide maximum suction and is designed to reduce trauma.
7. Enhance patients safety avoids disconnection from the ventilator during catheter change-out or untangling of lines.
8. Decrease accidental extubation ordecannulation during moving of the patient
9. Color coded rings provide fast size recognition.
Trifanz offers the rich choice of medical consumables to meet your clinical need. Welcome to contact us!
Closed Suction Tube,Closed Suction Catheter,Disposable Closed Suction Catheter,Closed Suction Tube System
Hangzhou Trifanz Medical Device Co., Ltd , https://www.cfzmeds.com