Application of Kangcheng Biochip Technology Service in Breast Cancer Tumor Metastasis Research
2023-01-21 11:09:49
Professor Sun Erwei of Sun Yat Sen Memorial Hospital Breast Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University is mainly engaged in the biological characteristics and therapeutic basic research of breast cancer. He has outstanding work in the research of non-coding RNA regulation of tumor invasion and metastasis and targeted introduction of small RNA to inhibit tumor metastasis. Recently, Professor Song Erwei's research team used RayBio Human Cytokine Antibody Array to reveal a new mechanism of breast cancer metastasis. Inflammatory factor chip screening revealed that EMT-producing breast cancer cells convert macrophages into tumor-associated macrophages by secreting the cytokine GM-CSF; tumor-associated macrophages secrete chemokine CCL18 to induce breast cancer cells. EMT and the secreted cytokine GM-CSF form a positive feedback loop that plays a crucial role in breast cancer metastasis. The research results were published in the international top journal Cancer Cell (impact factor 23.893). (Chip experiment provided by Kang Cheng technical service)
Research Background:
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor among women worldwide, and has become the first "killer" to endanger women's health. Breast cancer metastasis is the main cause of death in breast cancer patients. Research and treatment of breast cancer metastasis has become an important issue to improve the survival rate of breast cancer patients. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a key step in tumor metastasis in breast cancer. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the most abundant inflammatory cells in the tumor microenvironment and have important regulatory effects on tumor metastasis. Previous studies have found that EMT-producing tumor cells (mesenchymal-like tumor cells) and tumor-associated macrophages are at the forefront of tumor invasion, suggesting an interaction between the two. However, because of the difficulty of the tumor microenvironment in the body research, the conjecture has remained at the hypothesis level. Professor Song Erwei's research group aims to use the RayBio Human Cytokine Antibody Array to systematically study the interaction between tumor cells and TAMs.
Research ideas:
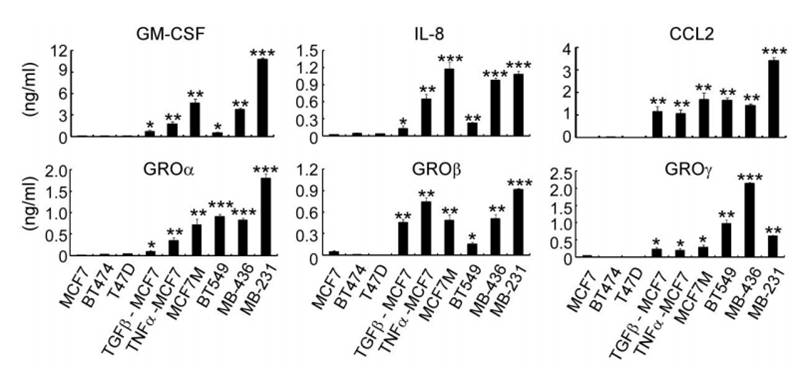
Professor Song Erwei's group of breast cancer cells and human primary macrophage co-culture models found that EMT-producing breast cancer cells (mesenchymal-like tumor cells) were more common than EMT-free breast cancer cells (epithelial tumor cells). Has the ability to activate macrophages to become TAMs. The authors used RayBio Human Cytokine Antibody Array to detect breast cancer cell culture supernatants with and without EMT. The results showed that GM-CSF , IL-8, CCL2, GROa, GROb and GROg were expressed in breast cancer cell samples with EMT. The level was significantly increased, and further verification found that only GM-CSF can activate macrophage to transform into TAMs under the synergistic action of lactic acid.
The preliminary experimental results of Professor Song's research group showed that TAMs can promote tumor metastasis. Treatment of epithelioid tumor cells with GM-CSF- activated macrophages allows the latter to transform into mesenchymal-like tumor cells. Among them, the chemokine CCL18 secreted by macrophages plays a key role in the EMT process. Studies have shown that CCL18 promotes NF-kB transcriptional activity by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which in turn induces EMT. A target gene of the transcription factor NF-kB is GM-CSF, which in turn activates tumor-associated macrophages, thereby forming a positive feedback loop.
Further, Professor Song's research team used a humanized mouse tumor model to find that inhibition of GM-CSF can effectively reduce the number of CCL18 + cells and inhibit tumor metastasis; and inhibition of CCL18 can reduce GM-CSF and inhibit tumor metastasis. These in vivo experiments demonstrated that CCL18 secreted by GM-CSF and TAMs secreted by tumor cells can form a positive feedback loop and promote breast cancer metastasis.
In addition, the authors analyzed the clinical specimens of more than 1000 breast cancers in China's three breast cancer centers and the international tumor database, confirmed that GM-CSF is positively correlated with CCL18 expression, and with cancer cell EMT phenotype, high pathological malignancy, three The subtype of vaginal breast cancer is closely related to the poor prognosis of patients.
In addition, the authors analyzed the clinical specimens of more than 1000 breast cancers in China's three breast cancer centers and the international tumor database, confirmed that GM-CSF is positively correlated with CCL18 expression, and with cancer cell EMT phenotype, high pathological malignancy, three The subtype of vaginal breast cancer is closely related to the poor prognosis of patients.
Technical route:

The results show:
A

B
C

A. RayBio Human Cytokine Antibody Array (inflammatory factor antibody chip) test results;
B. The differentially expressed cytokines screened by the ELISA were verified by the ELISA;
C. The cytokine GM-CSF and the chemokine CCL18 form a positive feedback loop-induced breast cancer metastasis model.
Significance:
This study reveals a new mechanism for tumor metastasis in breast cancer. Through breast cancer cell line and human primary macrophage co-culture model, it was first revealed that breast cancer cells with EMT had the ability to activate macrophages more than breast cancer cells without EMT. Inflammatory factor chip screening revealed that EMT-producing breast cancer cells activate macrophages by secreting the cytokine GM-CSF and a large amount of tumor metabolite lactic acid; macrophages secrete chemokine CCL18 to activate PI3K/Akt signaling. The pathway promotes NF-kB transcriptional activity, induces EMT in breast cancer cells and secretes cytokine GM-CSF, forming a positive feedback loop. This study explores the interrelationship between tumor cells and tumor microenvironment, and provides an important new direction for the in-depth exploration of breast cancer metastasis mechanisms and the discovery of new targets for treatment.
Original source:
A Positive Feedback Loop between Mesenchymal-like Cancer Cells and Macrophages Is Essential to Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell , 2014, 25(5): 605-620.
Please request the original text, please contact Kang Cheng sales engineer, or call the toll-free hotline; 800-820-5058
Another important function of amino acids is to provide energy to the human body. Normally, a healthy body on a general diet will use carbohydrates as its main fuel, but when the main source is depleted due to strenuous exercise, protein and amino acids can be used as a last resort. Amino acids also play an important role in food taste. Protein doesn't have much taste, but each amino acid has its own taste, and combining them is one of the important factors that define the taste of food
Amino Acid,Asn Amino Acid,Leucine Powder,Food Grade L-Tryptophan
YT(Xi'an) Biochem Co., Ltd. , https://www.ytwholefood.com